 |
Nikon Diaphot Transmitted Light Time Lapse Manual
last updated 8 June 2006
First, sign in the log book.
If you plan to use heater, you should turn it on and warm up
at least ONE hour before you start experiment.
This is critical for the microscope focus stability.

Turn on the ¡°BK Precision PowerSupply¡±.
Set voltage at 10 - 12 volts.
Do Not set highter than 12V!! The bulb will blow!!

Select objective lens:
| Lens Mag. | Phase Type | |
| 4x / 0.1 | N/A | |
| 10x / 0.3 | Phase 1 | |
| 20x / 0.4 | Phase 2 | |
| 40x / 0.55 * | Phase 3 | |
| 60x / 1.4 | Phase 4 |
Turn on the power of digital camera ¡°JVC AC ADAPTOR
AA-P700¡±.

Turn on ¡°PANASONIC MONITOR¡±.

Turn on PC, log in ¡°user¡± account.
Start program: ¡°Scion
Image¡±.

Now you are ready to start using the microscope. First, you need to select a lens by turning the turret manually, choose the appropriate contrast method from condenser turret.
Set up Kohler Illumination :
· Find your sample and focus on it with coarse and fine knob.
· Close the diaphragm of condenser to minimum, focus the diaphragm light image by raising or lowering the condenser, to let a sharp edged polygon appear in the field of view.
· Center the diaphragm image using the two large screws at the front of the condenser.
·
Open the luminous field diaphragm until it just disappears from your
field of view.
To collect a Single image :
Go to Special ¨C Video Control ¨C check Separate Sync box ¨C close this window. You can
collect a color image by checking Capture Color
Images box (the default setting is B/W).
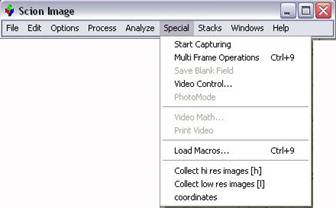
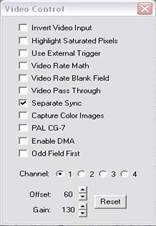
Go to Special ¨C Start Capturing , use Voltage knob on the ¡°BK Precision PowerSupply¡± to adjust the voltage between 10 ¨C 12v to get the best light intensity.
Just click Stop Capturing and save the picture on the screen as tif file.
To collect a movie :
· YOU CAN ONLY COLLECT BLACK/WHITE MOVIES
Two methods:
One: Scion Image build-in method
· Start capturing an image as described earlier, make a rectangle (ROI) on the previewing image. Make sure that you uncheck the
Capture Color Images box in the Video Control panel.
· Go to Stacks ¨C Make Movie
· Set variables for your movie, such as total frames and speed.
· Press OK to start shooting. It will stop automatically after all the frames have been collected.
· Don¡¯t forget to save the movie as tif file.
This method works only for a short time movie, means that the total frames should not be more than ???? because all the collected images are temporarily saved in the memory before it is saved into hard disk. If you have to collect long time movie, you¡¯d better use the second method ¨C run a macro program.
Two: Macro
·
Load the macro program. Go to Special ¨C Load Macros and choose ¡°segall high and low res collection macros jan 21 2004 movies¡±. Notice three functions appear at
the bottom.
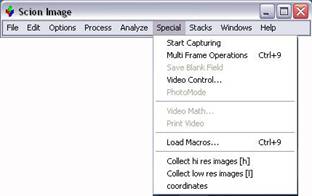
· Before running the macro, take a single image as described above and save it to the folder you want to save your movie file. This step prevents you from misplace your movie file. ( Another way is to copy the macro to your preferred folder and load it from that place)
· Create either high or low resolution movie by selecting a proper function (simply type ¡°h¡± or ¡°l¡± for shortcut). Follow the directions. The macro stops when all the images are collected. To stop macro before it finishes, type ¡°ESC¡± to cancel and all the collected images have been saved already.
· When macro finishes, you can save a copy of stack imaging file by closing the movie window and you¡¯ll be asked to save it. Please notice that there are two copies of your image data. One set is a series of single image tif files that are saved one by one during the program running. Another set is the image stack tif file that you save at last.
· Use ImageJ, DIAS for further analysis and animation.
Shut down :
Example Methods for a paper:
Longer version:
Cells were imaged by phase contrast with a Nikon Diaphot inverted microscope with a heated
chamber (Nikon, Melville, NY) and a JVC KY-F55B video camera (JVC, wherever, Japan) and
were digitized with a Scion LG-3 board and Scion Image software (Scion, Frederick,
Maryland) running on a Dell PC.
Shorter version:
Cells were imaged by phase contrast with a Nikon Diaphot inverted microscope with a heated
chamber (Nikon, Melville, NY).